Control response time
When controlling assets (EV's, batteries), the DemoBrandName ControllerDemoName sends a command to the device, which then needs time to process this command and adjust its state accordingly. This is known as the control response time. The time needed for this, and the time it takes for the DemoBrandName ControllerDemoName to send a new command, depends on the following factors:
- The type of device (e.g., battery, EV charger, heat pump)
- The settling check
- Limitation on the RS485 bus
- The scheduler interval
When your DemoBrandName ControllerDemoName is active in ancilllary services, a fast response time is crucial. On this page, we will explain how these factors influence the control response time and how you can optimize it for your specific use case.
Key takeaways:
- Don't use Modbus-RTU (RS485) when having multiple devices connected to the RS485 bus. Use Modbus-TCP instead.
- Disable ramp-up and ramp-down settings on devices that support it, such as batteries and inverters, to allow for faster response times.
- Disable settling check, if you understand the implications.
- Set the scheduler interval to 1 second for faster command processing.
For the full explanation of these factors, continue reading below.
The type of device
Different types of devices have inherently different response times due to their technical characteristics and communication protocols:
Battery and/or solar inverters (including hybrid inverters)
- Typically fast response times (1-5 seconds)
- Response time mainly depends on the inverter's internal controls
- May have built-in ramp rates for power transitions
EV Chargers
- Medium response time (5-15 seconds)
- Response depends on:
- Communication protocol (OCPP, Modbus, proprietary)
- Vehicle's charging capabilities
- Current charging state
- Must respect minimum charging current requirements
Heat Pumps
- Slower response times (30-180 seconds)
- Gradual power adjustments to protect the compressor
- Response time affected by:
- Operating mode (heating/cooling)
- Current temperature conditions
- Internal protection mechanisms
Relays and Switches
- Fast response times (1-5 seconds)
- Typically used for simple on/off control
For optimal control, consider the slowest responding device when setting up your control parameters. This ensures stable operation across all connected devices.
The 'Settling Check'
When working with multiple device brands, protocols, and models, patience becomes essential. Although devices like batteries, inverters, and EV chargers typically respond quickly to commands, they need time to update their measurements and send them back to the ControllerDemoName.
Two key factors affect response times:
- Energy meters may send data at slower rates, which means they don't immediately reflect the latest device actions
- Devices often need time to ramp up and stabilize to reach their target states
This is where settling checks become important. A settling check is a waiting period that ensures devices have fully reached their commanded states before new decisions are made. Think of it as letting the dust settle after a change. Without this mechanism, our control system could react to temporary states during the transition period. This would lead to unnecessary corrections - similar to trying to balance on a wobbling platform while constantly overcorrecting, making the situation worse.
Our implementation monitors three crucial aspects: First, it verifies that measurements are recent and reliable, ensuring we're not reacting to outdated information. Second, it tracks how power flows change over time, confirming that devices are responding as expected. Finally, it respects the inherent delays in device responses, giving equipment the time it needs to reach stable operation.
Consider a site with two devices: a modern battery system and an older heat pump. When we send a command to reduce power consumption by 5kW:
| Time | Battery | Heat Pump | System Response |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0:00 | 0kW | 5kW | Command sent: reduce by 5kW |
| 0:01 | -2kW | 5kW | Battery responds quickly |
| 0:03 | -2kW | 3kW | Heat pump starts responding |
| 0:05 | -2kW | 3kW | Waiting for stability |
| 0:07 | -2kW | 3kW | System confirms settled state |
The battery responds almost immediately, but the heat pump's older control system takes longer to adjust and report its new state. Without settling checks, we might misinterpret this delay as a failure to respond and send additional commands, potentially destabilizing the system. Instead, our controller patiently waits for all devices to report stable states before making any new decisions. The timeline for this exact flow then looks like this:
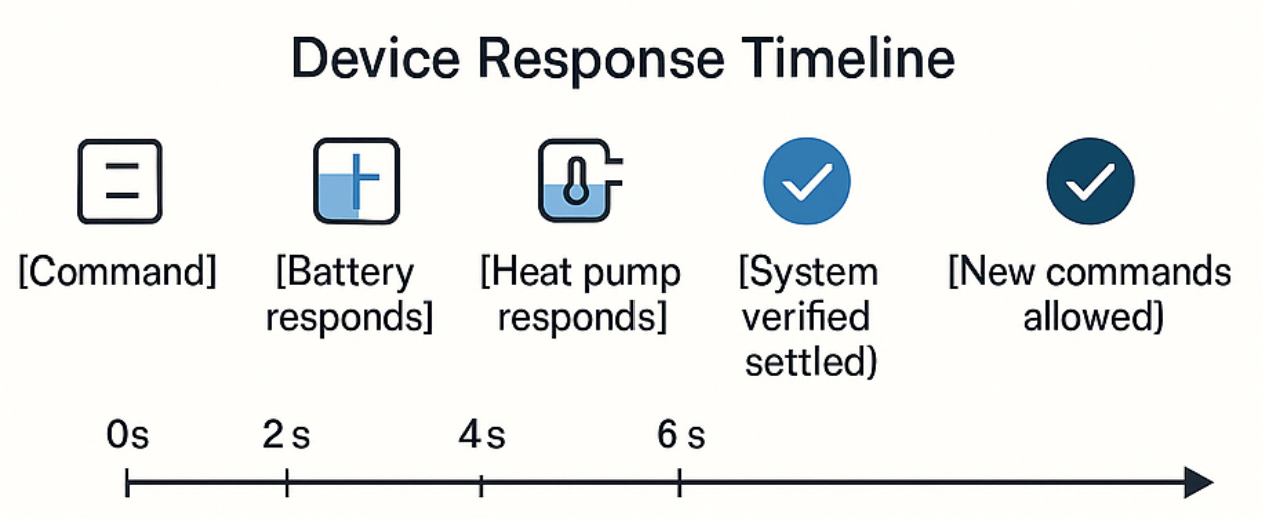
This measured approach might seem overly cautious, but in the world of power systems, stability and equipment longevity far outweigh the appeal of rapid-fire adjustments.
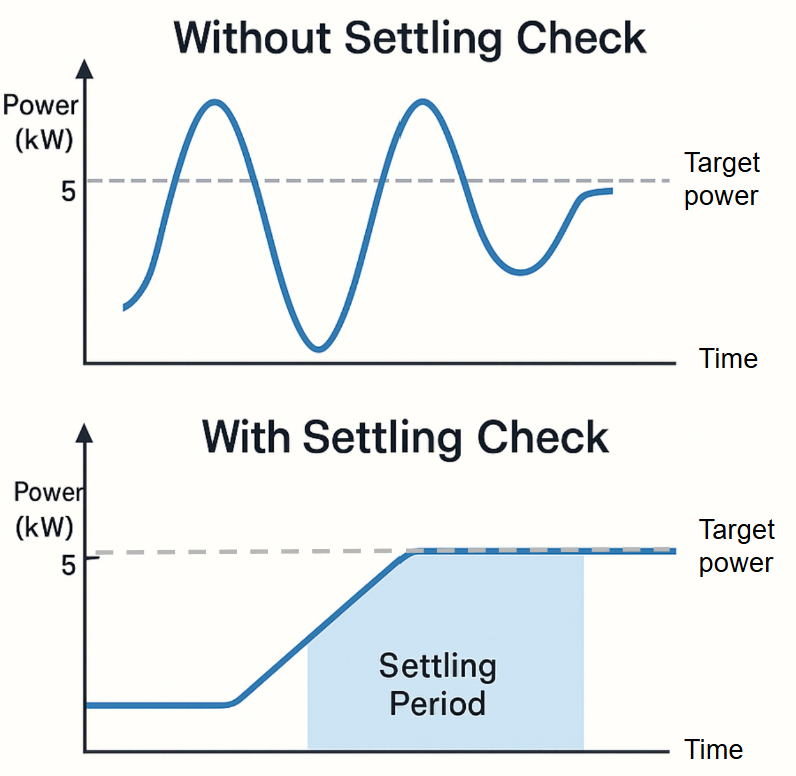
Disabling the settling check
- Disabling is not recommended and should only be done in exceptional cases. Otherwise, you risk destabilizing the system and causing oscillations.
- Proceed with causion and only if you fully understand the implications and prefer speed over stability.
The settling check can be disabled in the DemoBrandName ControllerDemoName app under the advanced settings. This will allow the controller to send commands without waiting for the devices to settle, potentially speeding up response time.
Click here to see the instructions
- Open the settings page:
- Change the "Enable device settling check" to
False:
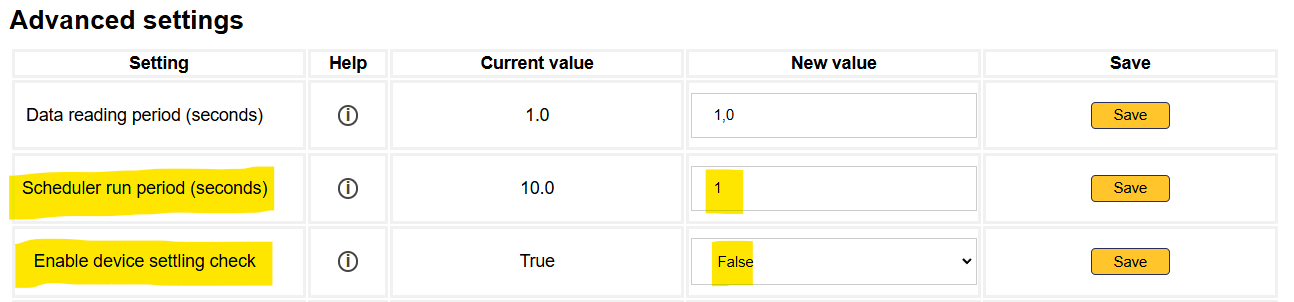
- Click on 'Save' to the right of the row.
Limitation on the RS485 bus
When multiple devices are connected to the RS485 bus, the control response time can be affected due to the inherent limitation of RS485 communication - only one device can communicate at a time.
As devices take turns communicating over the bus, each additional device increases the overall communication cycle time. This can lead to slower response times for all connected devices.
For optimal performance:
- Limit the number of devices to 5 or fewer per RS485 bus
- Use RS485 expansion accessories when connecting more devices
For detailed information about RS485 wiring and best practices, refer to the Wiring Best Practices guide.
Scheduler interval
The scheduler interval determines how often the DemoBrandName ControllerDemoName checks for new commands and sends them to the devices. A shorter interval allows for faster response times, while a longer interval can lead to delays in command execution. Check if the scheduler interval is set to a reasonable value for your use case. The default interval is 1 second, but you can adjust it in the advanced settings:
Click here to see the instructions
- Open the settings page:

- Change the "Enable device settling check" to
False:

- Click on 'Save' to the right of the row.